In accordance with recent research undertaken by HSBC, the UK economy is conditioned to devalue its currency in the long haul. HSBC argues that the UK economy does not have the wherewithal to bolster its currency over a multi-year period if it cannot overcome its reliance on imports, leaving the Pound dependent on the funds of foreign investors.
In accordance with recent research undertaken by HSBC, the UK economy is conditioned to devalue its currency in the long haul. HSBC argues that the UK economy does not have the wherewithal to bolster its currency over a multi-year period if it cannot overcome its reliance on imports, leaving the Pound dependent on the funds of foreign investors.
The United Kingdom is heavily dependent on imports, which means it buys more than it gets, which is a “core” economic factor for the pound.
“Build a robust foundation is equally essential for currencies. A reliable and secure source of financing gives a foundation for reduced vulnerability and, eventually, a solid foundation for a currency’s growth” Dominic Bunning, the chief of European FX study, explains.
“For both the euro and the pound, the outlook in this area is worse,” he argues.
Both the Eurozone and the United Kingdom confront severe cyclical tendencies, including declining GDP, rising inflation, and monetary policy constraints.
“However, the erosion in the core values of both currencies is turning out to be a more worrisome medium-term hazard,” adds Bunning.
He says that the underlying balance is the aggregate of current account flows and net Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and is considered a more steady stream of currency inflows. The Australian Dollar is an illustration of a fiat currency that continues to profit from its solid foundation. As Australia manages to ship iron ore, coal, and natural gas to the international economy, its trade surplus continues to grow.
In the meantime, the current account deficit of the United Kingdom has expanded as a result of the country’s increased purchases of such and the rest of the commodities. The Pound can only sustain its worth if this deficit is compensated by other sources, often by overseas investors seeking to acquire British assets.
Ex-Bank of England Governor Mark Carney referred to this as “the compassion of outsiders” when describing this risky flow for the British pound. “However, the Eurozone has now begun to experience similar unfavorable trends.”
In the past one-and-a-half years, the Eurozone’s core balance has shifted from a surplus of over 4% of GDP to a shortfall of 1% of GDP.
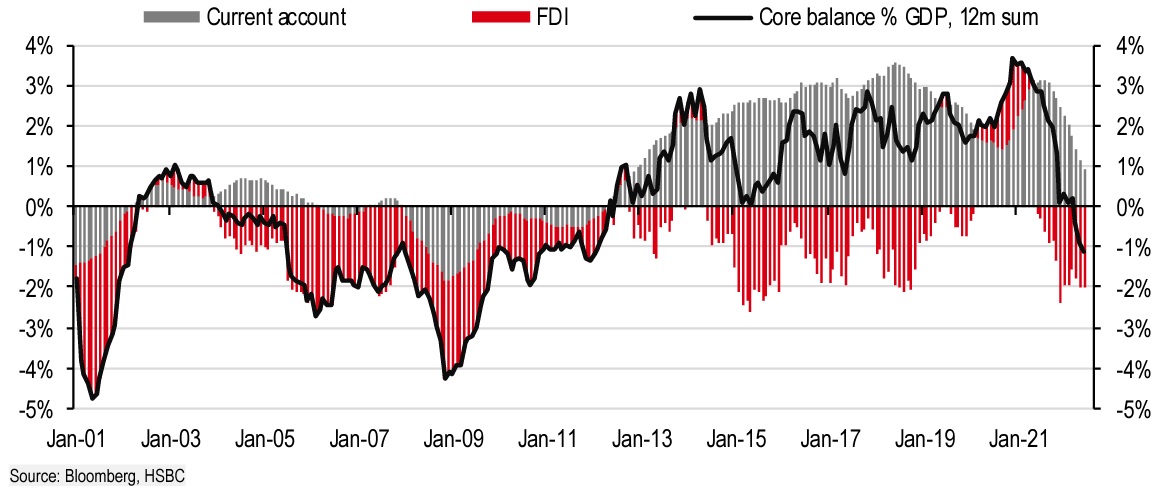
As the fundamental balance worsened, the Euro-Dollar exchange rate reached parity. In the past, the Eurozone has depended on Germany’s export acumen to record current account surpluses, but this has altered this year due to a decline in worldwide demand.
As a result of Russia’s assault on Ukraine, the cost of purchasing carbon fuels and commodities has skyrocketed, driving up the current account imbalance. However, this issue has plagued the United Kingdom for several years.
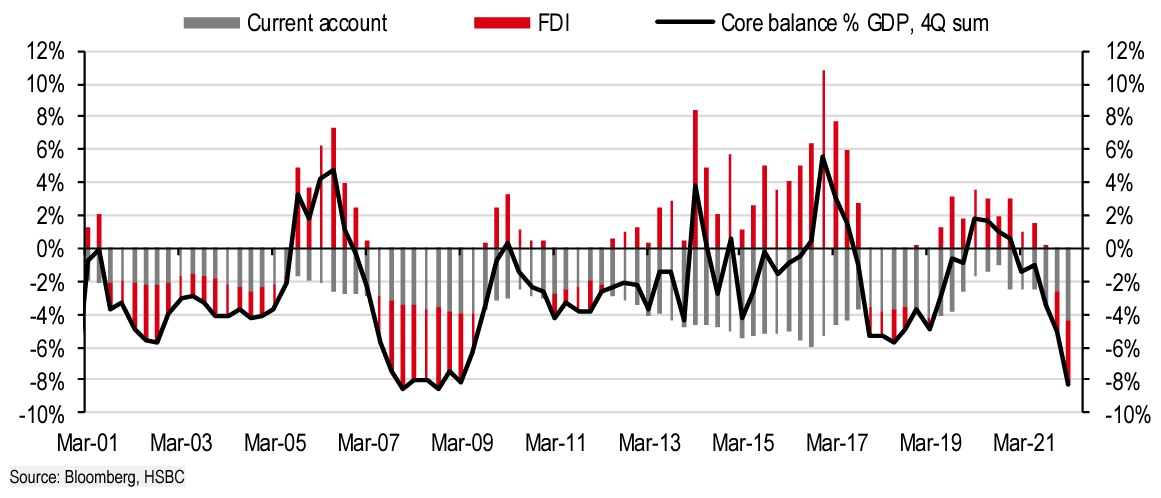
“In the past two years, the United Kingdom has gone from an excess of 2% of GDP to a shortfall of 8% of GDP,” adds Bunning. In Quarter 1, the ONS (Office for National Statistics) reported that the UK’s fundamental current account deficit, barring precious metals, grew to £44.2 billion, or 7.1% of total GDP.
This was mostly a result of the country’s trade imbalance, which was a result of its continued reliance on commodity and commodities imports and failure to export on a significant scale. Given that this position is unlikely to improve for several years, the gap is expected to remain a continuous aspect of the British economy.
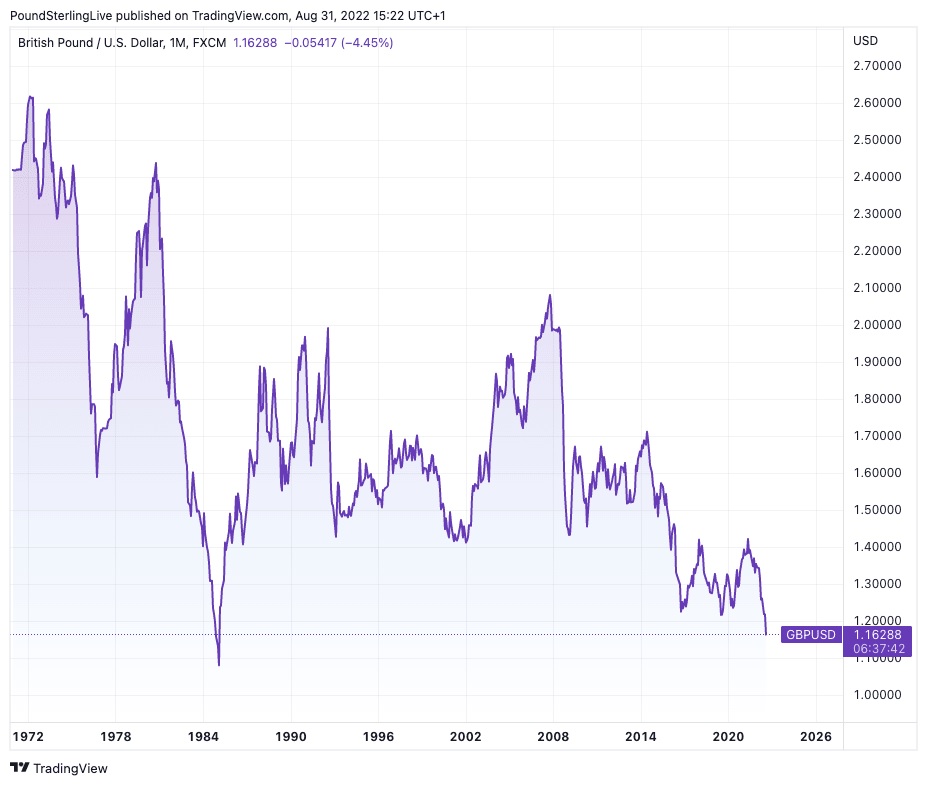
All of this bodes ill for the Pound. “These deficits must be financed outside. This is not a problem in of itself, but for the EUR and GBP, these flows may be more erratic and susceptible to external variables” asserts Bunning. During the first quarter of 2022, the United Kingdom’s financial account reported a net inflow of £29.6 billion as liabilities climbed higher than assets.
This shows that there is a short-term asymmetry threat to the negative for both currencies in the context of tightening global finance constraints and declining global risk appetite, according to Bunning. “These systemic disparities necessitate currency depreciation over time,” he continues.
This might assist to understand why the Pound has maintained a multi-decade downward trend relative to the Dollar: According to the research of HSBC, this pattern of depreciation versus the Dollar will persist and a trial of parity and ultimate slide to the downside is expected in the next years.
“On an extended viewpoint, the deterioration of the core balances implies that both currencies are not undervalued,” adds Bunning. “A downward overrun may be larger than we had previously anticipated.”
Given that the Eurozone suffers comparable “core” difficulties to the United Kingdom, the Pound to Euro currency conversion rate may be more steady over the long run. Nevertheless, the Euro may receive momentum if the Eurozone economy were to begin operating at full capacity once more.