The Australian Dollar remains the top performing major currency so far this week following the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) announcement that it will begin tapering its asset purchase initiative in response to the economy’s continued growth.
The Australian Dollar remains the top performing major currency so far this week following the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) announcement that it will begin tapering its asset purchase initiative in response to the economy’s continued growth.
The Australian Dollar rose versus the Euro, the Pound, the US Dollar, and other currencies after the Reserve Bank of Australia announced that it would cut the quantum of Australian government bonds it buys as portion of its quantitative easing program. The RBA had been purchasing A$5 billion in bonds on a weekly basis, but announced on Tuesday that it will cut this to A$4 billion, beginning November 11.
The shift is a hint to the foreign exchange market that the RBA is nearing the end of its unprecedented stimulus plan, which experts credit with keeping the Australian Dollar’s value low. “These measures assist in the reduction of loan rates in the economy. They also lead to a softer Australian currency than would otherwise be the situation” Besa Deda, Chief Economist at Sydney’s St. George Bank, agrees. The fact that these programs will be phased out over the next months is thus positive for the Australian Dollar:
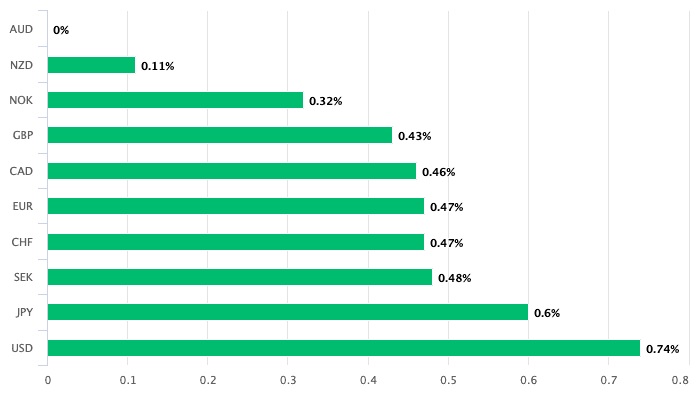
The British Pound to Australian Dollar exchange rate decreased 0.40% to 1.8295, while the Australian Dollar to US Dollar exchange rate gained 0.80% to 0.7592. The resurgence of additional Covid-19 instances in Australia and consequent lockdowns was one source of concern for the RBA, but the bank is content to look past the short-term problem by these outbreaks.
“The impact of recent viral outbreaks and lockdowns is a near-term unknown. However, past experience has shown that once epidemics are managed and limitations are lifted, the economy swiftly recovers” Governor Philip Lowe made the announcement in a statement. After all, the RBA stated in a statement that the economy is in good shape:
“The unemployment rate fell to 5.1% in May, and there are now more Australians working than there were before the epidemic.” The RBA also expressed satisfaction with the decrease in underemployment, noting that workforce participation is at historic levels. The RBA decided to ‘taper’ its quantitative easing operation as a result of this resilience. “The Board is modifying the weekly amount acquired in response to the better-than-anticipated economic rebound and enhanced forecasts,” stated Lowe.
The Reserve Bank of Australia will now switch from a strategy of locking in the whole target amount of bond buying under its quantitative easing plan to a more fluid week-by-week strategy. This will enable the RBA to terminate its quantitative easing strategy when necessary, as predicted by the market. What the market did not anticipate, nevertheless, is the move to cut the weekly bond purchase amount from A$5 billion to A$4 billion, which is regarded as a form of backing for the Australian Dollar.
Bill Evans, Westpac’s Chief Economist, said, “The policy is a stricter strategy than we had envisaged.” As a result, the RBA’s quantitative easing program would acquire up to A$40 billion in bonds, which is much lower than the market anticipated.
In the meantime, the RBA’s Yield Curve Control (YCC) program, which is part of the asset purchase initiative, has decided to maintain targeting the April 2024 bond. There was a chance that the RBA would start purchasing the November 2024 bond, which some saw as a dovish hint that might have spurred Aussie Dollar depreciation.
“Not extending the Yield Curve Target plan to the November 2024 bonds is a choice to tighten strategy even further,” Evans adds. Westpac predicts that the RBA will stop purchasing assets by 2022. The Federal Reserve of the United States is expected to reveal its plan to start reducing its bond buying in September, with a climb date in early January and a timeline of mid-2022, according to Westpac. “Once the FED’s initiatives are in place, they will provide protection for the RBA if it decides to reduce its buying even sooner than we estimate, approximately mid-2022,” Evans adds.
The RBA’s July announcement was more hawkish than expected, according to Westpac, and is congruent with their prediction that the very first rate increase will occur in March 2023, considerably sooner than the RBA’s present “central scenario” of a rate increase in 2024.