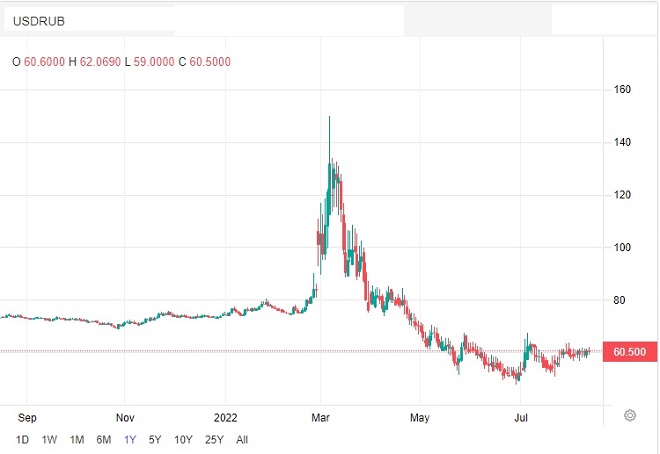
As per the Bank of Russia’s macroeconomic forecast, the USD/RUB exchange rate is projected to average 70.4, 75.0, and 80.0 in 2023-2025. Presently, the USD/RUB exchange rate is at 60.50. Nevertheless, the most recent economic data shows that the ruble would certainly depreciate in the next months.
As per the Bank of Russia’s macroeconomic forecast, the USD/RUB exchange rate is projected to average 70.4, 75.0, and 80.0 in 2023-2025. Presently, the USD/RUB exchange rate is at 60.50. Nevertheless, the most recent economic data shows that the ruble would certainly depreciate in the next months.
In the June 2022 quarter, Russia’s gross domestic product contracted by 4% compared to the same period the previous year, as a result of the Russia-Ukraine conflict and accompanying western sanctions, according to early estimates. The central bank of Russia predicted that the economy would drop by 4.3% in the second quarter and by 7% in the third quarter. The central bank forecast in April that the economy will contract by 4% to 6% in 2022 and begin to recover in the second half of 2023.
In July 2022, the annual inflation rate in Russia decreased to 15.1%, down from 15.9% the previous month and below market estimates of 15.3%. It was the lowest inflation rate since March when it entered double-digit territory. However, food costs continued to grow substantially (16.8 percent), followed by non-food items (16.5 percent) and then services (10.8 percent). Consumer prices fell 0.39 percent on a monthly basis, following a 0.35 percent loss in June and declining more than expected by 0.2 percent. In contrast, core consumer prices continued to rise quicker than inflationary pressures, at 18.4% from July 2021 to July 2022.
After reaching historic highs since the attack of Ukraine, Russia’s current-account excess more than quadrupled from the previous year, as import decreases coincided with surging profits from energy and commodities exports.
The current account surplus, the biggest gauge of trade and investment flows, rose to more than $167 billion in January-July versus just more than $50 billion in the corresponding period in 2021, according to a preliminary estimate released by the Bank of Russia on Tuesday.
Since the launch of attack in February, the revenues have become a crucial source of hard money for the Kremlin. War-related western sanctions have led to a decline in imports, which has resulted in a surplus. The provisional amount for the initial six months of 2022 was $138,5 billion.
Nevertheless, Russia is anticipated to face a fiscal deficit. It is conceivable to create a “press” to tackle the issue of a shortage of budget money for the growth of the economy under sanctions. Eduard Rossel, a senator from the Sverdlovsk area and member of the Sovfeda committee on the budget and financial markets, voiced this position on Thursday’s broadcast of the Moscow radio station “Govorit Moscow.”
As per him, we’re discussing an annual amount of 5 trillion rubles – a sum that the ministries and departments have asked for in addition to the sums already granted for the upcoming three years (15 trillion rubles in total).
In accordance with the Ministry of Finance’s projections, the budget deficit for this year would be 1,6 trillion rubles, rising to 6 trillion rubles by 2025. (cumulative total). The government formed the National Welfare Fund and a debt issuance that must be acquired only by Russian investors to fund it.